
[ad_1]
Maintaining with an trade as fast-moving as AI is a tall order. So till an AI can do it for you, right here’s a useful roundup of current tales on the earth of machine studying, together with notable analysis and experiments we didn’t cowl on their very own.
This week in AI, I’d like to show the highlight on labeling and annotation startups — startups like Scale AI, which is reportedly in talks to boost new funds at a $13 billion valuation. Labeling and annotation platforms won’t get the eye flashy new generative AI fashions like OpenAI’s Sora do. However they’re important. With out them, fashionable AI fashions arguably wouldn’t exist.
The information on which many fashions prepare needs to be labeled. Why? Labels, or tags, assist the fashions perceive and interpret information in the course of the coaching course of. For instance, labels to coach a picture recognition mannequin may take the type of markings round objects, “bounding bins” or captions referring to every individual, place or object depicted in a picture.
The accuracy and high quality of labels considerably affect the efficiency — and reliability — of the skilled fashions. And annotation is an unlimited endeavor, requiring 1000’s to thousands and thousands of labels for the bigger and extra refined information units in use.
So that you’d assume information annotators can be handled effectively, paid dwelling wages and given the identical advantages that the engineers constructing the fashions themselves get pleasure from. However usually, the alternative is true — a product of the brutal working situations that many annotation and labeling startups foster.
Firms with billions within the financial institution, like OpenAI, have relied on annotators in third-world international locations paid only some {dollars} per hour. A few of these annotators are uncovered to extremely disturbing content material, like graphic imagery, but aren’t given time without work (as they’re normally contractors) or entry to psychological well being assets.
A wonderful piece in NY Magazine peels again the curtains on Scale AI particularly, which recruits annotators in international locations as far-flung as Nairobi and Kenya. A few of the duties on Scale AI take labelers a number of eight-hour workdays — no breaks — and pay as little as $10. And these employees are beholden to the whims of the platform. Annotators typically go lengthy stretches with out receiving work, or they’re unceremoniously booted off Scale AI — as occurred to contractors in Thailand, Vietnam, Poland and Pakistan lately.
Some annotation and labeling platforms declare to supply “fair-trade” work. They’ve made it a central a part of their branding in actual fact. However as MIT Tech Overview’s Kate Kaye notes, there aren’t any rules, solely weak trade requirements for what moral labeling work means — and firms’ personal definitions differ extensively.
So, what to do? Barring an enormous technological breakthrough, the necessity to annotate and label information for AI coaching isn’t going away. We are able to hope that the platforms self-regulate, however the extra real looking answer appears to be policymaking. That itself is a tough prospect — nevertheless it’s the very best shot we’ve, I’d argue, at altering issues for the higher. Or at the least beginning to.
Listed here are another AI tales of notice from the previous few days:
-
- OpenAI builds a voice cloner: OpenAI is previewing a brand new AI-powered device it developed, Voice Engine, that permits customers to clone a voice from a 15-second recording of somebody talking. However the firm is selecting to not launch it extensively (but), citing dangers of misuse and abuse.
- Amazon doubles down on Anthropic: Amazon has invested an additional $2.75 billion in rising AI energy Anthropic, following via on the choice it left open final September.
- Google.org launches an accelerator: Google.org, Google’s charitable wing, is launching a brand new $20 million, six-month program to assist fund nonprofits growing tech that leverages generative AI.
- A brand new mannequin structure: AI startup AI21 Labs has launched a generative AI mannequin, Jamba, that employs a novel, new(ish) mannequin structure — state area fashions, or SSMs — to enhance effectivity.
- Databricks launches DBRX: In different mannequin information, Databricks this week launched DBRX, a generative AI mannequin akin to OpenAI’s GPT collection and Google’s Gemini. The corporate claims it achieves state-of-the-art outcomes on a variety of fashionable AI benchmarks, together with a number of measuring reasoning.
- Uber Eats and UK AI regulation: Natasha writes about how an Uber Eats courier’s struggle towards AI bias exhibits that justice below the UK’s AI rules is difficult gained.
- EU election safety steerage: The European Union revealed draft election safety pointers Tuesday aimed on the round two dozen platforms regulated below the Digital Companies Act, together with pointers pertaining to stopping content material advice algorithms from spreading generative AI-based disinformation (aka political deepfakes).
- Grok will get upgraded: X’s Grok chatbot will quickly get an upgraded underlying mannequin, Grok-1.5 — on the similar time all Premium subscribers on X will acquire entry to Grok. (Grok was beforehand unique to X Premium+ prospects.)
- Adobe expands Firefly: This week, Adobe unveiled Firefly Companies, a set of greater than 20 new generative and inventive APIs, instruments and companies. It additionally launched Customized Fashions, which permits companies to fine-tune Firefly fashions based mostly on their property — part of Adobe’s new GenStudio suite.
Extra machine learnings
How’s the climate? AI is more and more capable of let you know this. I famous just a few efforts in hourly, weekly, and century-scale forecasting just a few months in the past, however like all issues AI, the sphere is shifting quick. The groups behind MetNet-3 and GraphCast have revealed a paper describing a brand new system referred to as SEEDS, for Scalable Ensemble Envelope Diffusion Sampler.
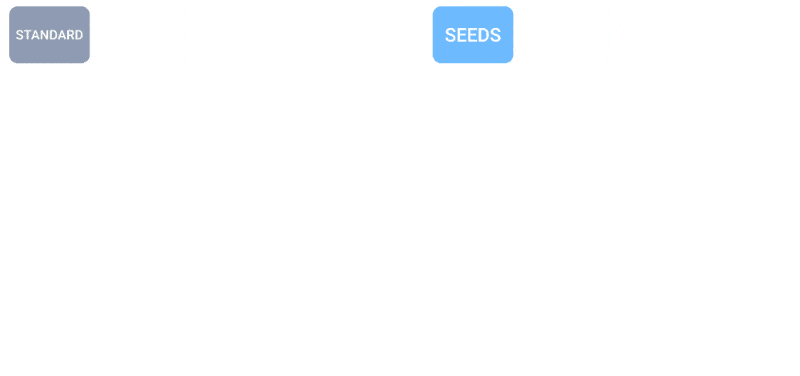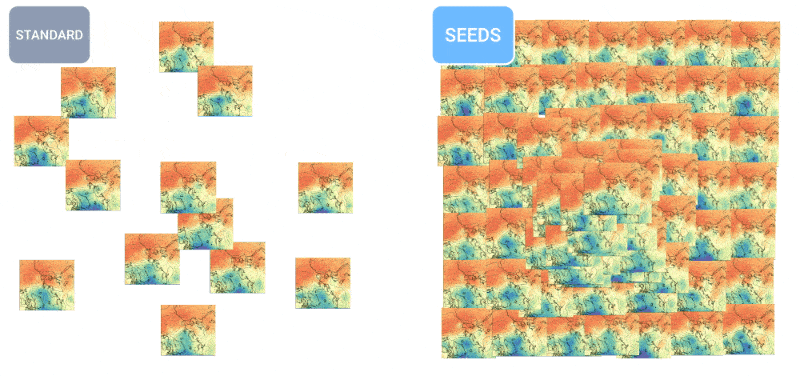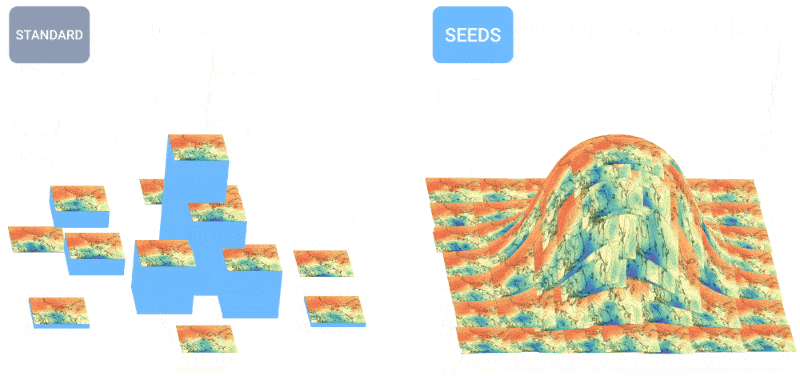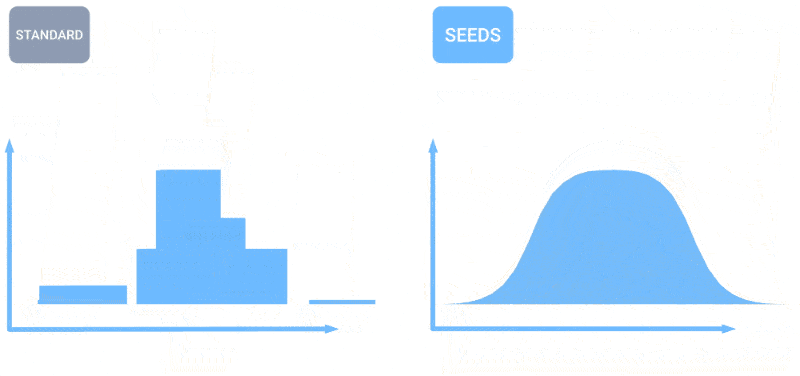
Animation displaying how extra predictions creates a extra even distribution of climate predictions.
SEEDS makes use of diffusion to generate “ensembles” of believable climate outcomes for an space based mostly on the enter (radar readings or orbital imagery maybe) a lot sooner than physics-based fashions. With larger ensemble counts, they will cowl extra edge circumstances (like an occasion that solely happens in 1 out of 100 doable situations) and be extra assured about extra possible conditions.
Fujitsu can be hoping to higher perceive the pure world by making use of AI picture dealing with methods to underwater imagery and lidar information collected by underwater autonomous automobiles. Bettering the standard of the imagery will let different, much less refined processes (like 3D conversion) work higher on the goal information.
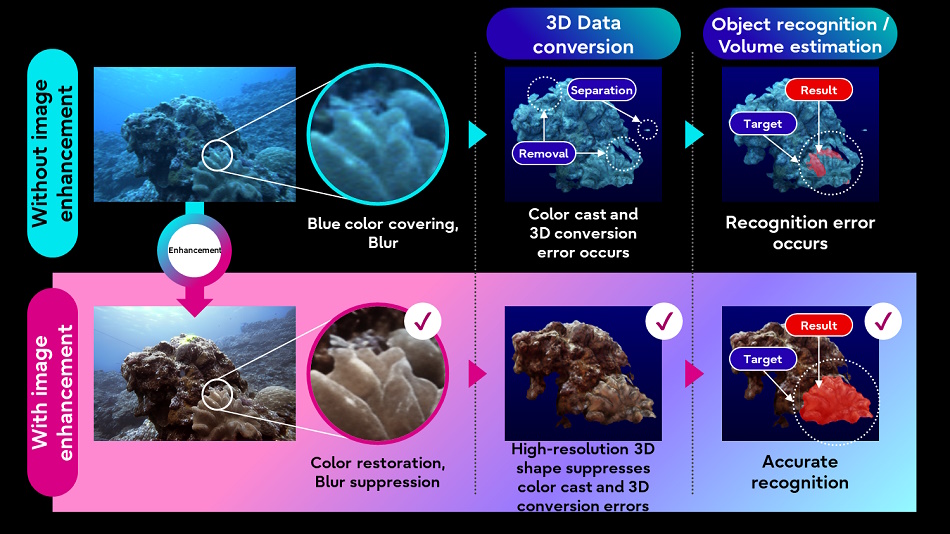
Picture Credit: Fujitsu
The concept is to construct a “digital twin” of waters that may assist simulate and predict new developments. We’re a great distance off from that, however you gotta begin someplace.
Over among the many LLMs, researchers have discovered that they mimic intelligence by a good easier than anticipated methodology: linear features. Frankly the maths is past me (vector stuff in lots of dimensions) however this writeup at MIT makes it fairly clear that the recall mechanism of those fashions is fairly… primary.
Regardless that these fashions are actually difficult, nonlinear features which are skilled on plenty of information and are very exhausting to know, there are typically actually easy mechanisms working inside them. That is one occasion of that,” mentioned co-lead writer Evan Hernandez. In case you’re extra technically minded, take a look at the paper right here.
A technique these fashions can fail is just not understanding context or suggestions. Even a extremely succesful LLM won’t “get it” in case you inform it your title is pronounced a sure approach, since they don’t really know or perceive something. In circumstances the place that is perhaps vital, like human-robot interactions, it may put individuals off if the robotic acts that approach.
Disney Analysis has been trying into automated character interactions for a very long time, and this title pronunciation and reuse paper simply confirmed up a short time again. It appears apparent, however extracting the phonemes when somebody introduces themselves and encoding that slightly than simply the written title is a great strategy.

Picture Credit: Disney Analysis
Lastly, as AI and search overlap an increasing number of, it’s value reassessing how these instruments are used and whether or not there are any new dangers introduced by this unholy union. Safiya Umoja Noble has been an vital voice in AI and search ethics for years, and her opinion is all the time enlightening. She did a pleasant interview with the UCLA information crew about how her work has advanced and why we have to keep frosty with regards to bias and unhealthy habits in search.
[ad_2]