
[ad_1]
Abstract: Historic viruses performed a pivotal function within the improvement of myelin, essential for complicated vertebrate brains. The invention of “RetroMyelin,” a retrovirus-derived factor important for myelin manufacturing throughout mammals, amphibians, and fish, underscores the affect of viral genes on vertebrate evolution.
The research demonstrates that myelination, a key think about nerve impulse conduction and vertebrate range, owes its existence to historical viral insertions, difficult earlier understandings of evolutionary biology. This convergence of virology and neurobiology opens new avenues for exploring the molecular mechanisms behind evolution and the intricate relationship between viruses and vertebrate improvement.
Key Information:
- “RetroMyelin,” a gene sequence derived from historical retroviruses, is significant for the manufacturing of myelin in vertebrates.
- The presence of RetroMyelin in various vertebrate teams suggests separate viral genome integration occasions, highlighting its function in convergent evolution.
- Experimental disruption of RetroMyelin in zebrafish and frogs led to considerably lowered myelin manufacturing, proving its practical function in myelination.
Supply: Cell Press
Researchers report February 15 within the journal Cell that historical viruses could also be to thank for myelin—and, by extension, our giant, complicated brains.
The crew discovered {that a} retrovirus-derived genetic factor or “retrotransposon” is important for myelin manufacturing in mammals, amphibians, and fish. The gene sequence, which they dubbed “RetroMyelin,” is probably going a results of historical viral an infection, and comparisons of RetroMyelin in mammals, amphibians, and fish counsel that retroviral an infection and genome-invasion occasions occurred individually in every of those teams.
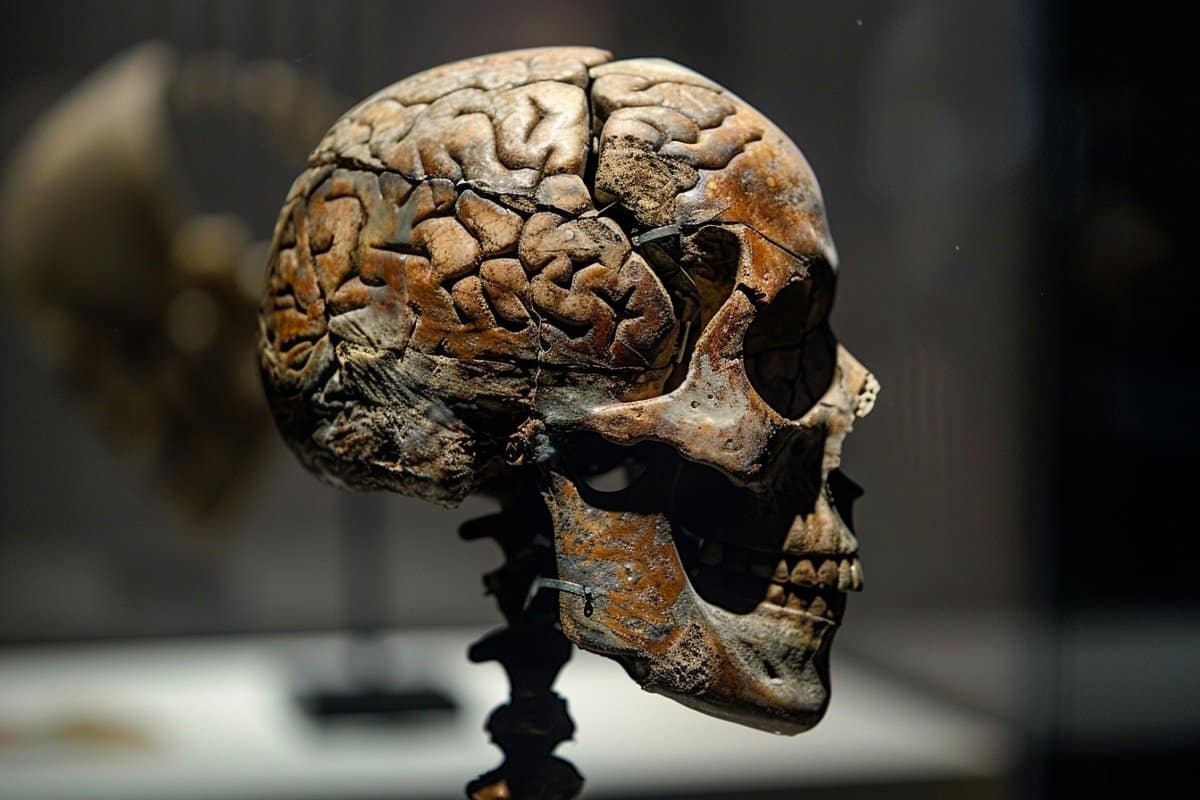
“Retroviruses have been required for vertebrate evolution to take off,” says senior writer and neuroscientist Robin Franklin of Altos Labs-Cambridge Institute of Science.
“If we didn’t have retroviruses sticking their sequences into the vertebrate genome, then myelination wouldn’t have occurred, and with out myelination, the entire range of vertebrates as we all know it will by no means have occurred.”
Myelin is a fancy, fatty tissue that ensheathes vertebrate nerve axons. It allows speedy impulse conduction without having to extend axonal diameter, which implies nerves may be packed nearer collectively. It additionally supplies metabolic help to nerves, which implies nerves may be longer.
Myelin first appeared within the tree of life across the identical time as jaws, and its significance in vertebrate evolution has lengthy been acknowledged, however till now, it was unclear what molecular mechanisms triggered its look.
The researchers observed RetroMyelin’s function in myelin manufacturing after they have been analyzing the gene networks utilized by oligodendrocytes, the cells that produce myelin within the central nervous system.
Particularly, the crew was investigating the function of noncoding areas together with retrotransposons in these gene networks—one thing that hasn’t beforehand been explored within the context of myelin biology.
“Retrotransposons compose about 40% of our genomes, however nothing is thought about how they may have helped animals purchase particular traits throughout evolution,” says first writer Tanay Ghosh, a computational biologist at Altos Labs-Cambridge Institute of Science.
“Our motivation was to know the way these molecules are serving to evolutionary processes, particularly within the context of myelination.”
In rodents, the researchers discovered that the RNA transcript of RetroMyelin regulates the expression of myelin primary protein, one of many key parts of myelin. After they experimentally inhibited RetroMyelin in oligodendrocytes and oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (the stem cells from which oligodendrocytes are derived), the cells may not produce myelin primary protein.
To look at whether or not RetroMyelin is current in different vertebrate species, the crew looked for related sequences throughout the genomes of jawed vertebrates, jawless vertebrates, and several other invertebrate species.
They recognized analogous sequences in all different courses of jawed vertebrates (birds, fish, reptiles, and amphibians) however didn’t discover a related sequence in jawless vertebrates or invertebrates.
“There’s been an evolutionary drive to make impulse conduction of our axons faster as a result of having faster impulse conduction means you possibly can catch issues or flee from issues extra quickly,” says Franklin.
Subsequent, the researchers wished to know whether or not RetroMyelin was included as soon as into the ancestor of all jawed vertebrates or whether or not there have been separate retroviral invasions within the totally different branches.
To reply these questions, they constructed a phylogenetic tree from 22 jawed vertebrate species and in contrast their RetroMyelin sequences. The evaluation revealed that RetroMyelin sequences have been extra related inside than between species, which means that RetroMyelin was acquired a number of instances by means of the method of convergent evolution.
The crew additionally confirmed that RetroMyelin performs a practical function in myelination in fish and amphibians. After they experimentally disrupted the RetroMyelin gene sequence within the fertilized eggs of zebrafish and frogs, they discovered that the growing fish and tadpoles produced considerably much less myelin than regular.
The research highlights the significance of non-coding areas of the genome for physiology and evolution, the researchers say. “Our findings open up a brand new avenue of analysis to discover how retroviruses are extra typically concerned in directing evolution,” says Ghosh.
Funding:
This analysis was supported by the Adelson Medical Analysis Basis, the UK A number of Sclerosis Society, the Wellcome Belief, and the Altos Labs-Cambridge Institute of Science.
About this evolutionary neuroscience analysis information
Creator: Kristopher Benke
Supply: Cell Press
Contact: Kristopher Benke – Cell Press
Picture: The picture is credited to Neuroscience Information
Unique Analysis: Open entry.
“A retroviral hyperlink to vertebrate myelination by means of retrotransposon RNA-mediated management of myelin gene expression” by Robin Franklin et al. Cell
Summary
A retroviral hyperlink to vertebrate myelination by means of retrotransposon RNA-mediated management of myelin gene expression
Highlights
- RNA expression of retroviral factor RNLTR12-int is essential for myelination
- RNLTR12-int binds to SOX10 to manage Mbp expression
- RNLTR12-int-like sequences (RetroMyelin) have been recognized in all jawed vertebrates
- Convergent evolution seemingly led to RetroMyelin acquisition, tailored for myelination
Abstract
Myelin, the insulating sheath that surrounds neuronal axons, is produced by oligodendrocytes within the central nervous system (CNS). This evolutionary innovation, which first seems in jawed vertebrates, enabled speedy transmission of nerve impulses, extra complicated brains, and larger morphological range.
Right here, we report that RNA-level expression of RNLTR12-int, a retrotransposon of retroviral origin, is important for myelination. We present that RNLTR12-int-encoded RNA binds to the transcription issue SOX10 to manage transcription of myelin primary protein (Mbp, the foremost constituent of myelin) in rodents. RNLTR12-int-like sequences (which we identify RetroMyelin) are present in all jawed vertebrates, and we additional reveal their perform in regulating myelination in two totally different vertebrate courses (zebrafish and frogs).
Our research subsequently means that retroviral endogenization performed a outstanding function within the emergence of vertebrate myelin.
[ad_2]