
[ad_1]
Abstract: Researchers uncovered the connection between people’ drawings and their arithmetic problem-solving methods. By analyzing the illustrations produced by each youngsters and adults when tasked with fixing easy mathematical issues, the analysis workforce found that sure forms of drawings correlate with essentially the most environment friendly calculation strategies.
This discovering means that visible representations can considerably affect one’s skill to plan and apply optimum options to arithmetic challenges. The examine not solely highlights the enduring distinction between cardinal and ordinal problem-solving approaches but in addition proposes drawing evaluation as a novel methodology to boost mathematical studying and instruction.
Key Information:
- Impression of Visible Representations: The examine revealed that the character of drawings, whether or not cardinal or ordinal, influences the number of calculation methods, with ordinal representations usually resulting in extra direct options.
- Age-Impartial Findings: Related outcomes had been noticed amongst each adults and youngsters, indicating that the affect of visible representations on problem-solving transcends age and expertise.
- Pedagogical Implications: The analysis means that analyzing college students’ drawings may present educators with insights into their understanding and illustration of mathematical issues, providing a brand new avenue for optimizing instructing methods.
Supply: College of Geneva
Fixing arithmetic issues, even easy subtractions, includes psychological representations whose affect stays to be clarified. Visualizing these representations would allow us to higher perceive our reasoning and adapt our instructing strategies.
A workforce from the College of Geneva (UNIGE), in collaboration with CY Cergy Paris College (CYU) and College of Burgundy (uB), analyzed drawings made by youngsters and adults when fixing easy issues. The scientists discovered that, regardless of the age of the participant, the best calculation methods had been related to sure drawing typologies.
These outcomes, revealed within the journal Reminiscence & Cognition, open up new views for the instructing of arithmetic.
Studying arithmetic usually includes small issues, linked to concrete on a regular basis conditions. For instance, pupils have so as to add up portions of flour to make a recipe or subtract sums of cash to search out out what’s left of their wallets after procuring. They’re thus led to translate statements into algorithmic procedures to search out the answer.
This translation of phrases into fixing methods includes a stage of psychological illustration of mathematical info, akin to numbers or the arithmetic operation to be carried out, and non-mathematical info, such because the context of the issue.
The cardinal or ordinal dimensions of issues
Having a clearer thought of those psychological representations would allow a greater understanding of the selection of calculation methods. Scientists from UNIGE, CYU and uB performed a examine with 10-year-old youngsters and adults, asking them to resolve easy issues with the instruction to make use of as few calculation steps as doable.
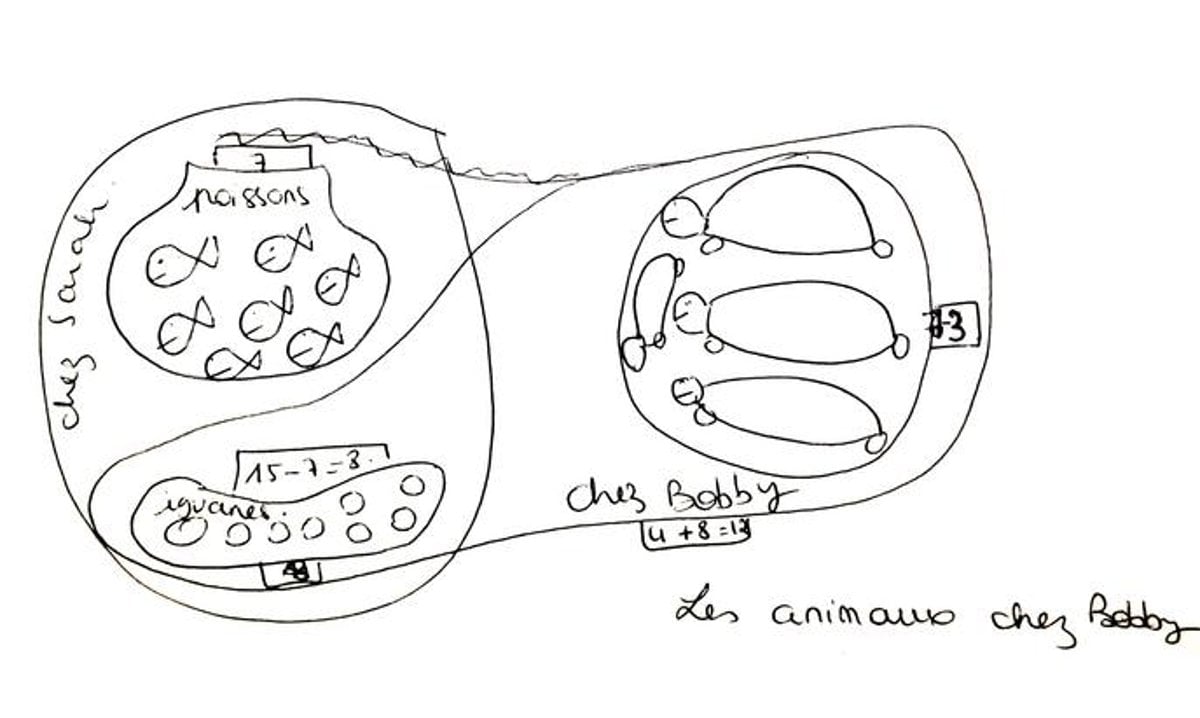
The individuals had been then requested to supply a drawing or diagram explaining their problem-solving technique for every assertion. The contexts of some issues known as on the cardinal properties of numbers – the amount of components in a set – others on their ordinal properties – their place in an ordered checklist.
The previous concerned marbles, fishes, or books, for instance: ‘‘Paul has 8 pink marbles. He additionally has blue marbles. In complete, Paul has 11 marbles. Jolene has as many blue marbles as Paul, and a few inexperienced marbles. She has 2 inexperienced marbles lower than Paul has pink marbles. In complete, what number of marbles does Jolene have?’’.
The latter concerned lengths or durations, for instance: ‘‘Sofia traveled for 8 hours. Her journey began through the day. Sofia arrived at 11. Fred leaves similtaneously Sofia. Fred’s journey lasted 2 hours lower than Sofia’s. What time was it when Fred arrived?”
Each of the above issues share the identical mathematical construction, and each may be solved by a protracted technique in 3 steps: 11 – 8 = 3; 8 – 2 = 6; 6 + 3 = 9, but in addition in a single calculation: 11 – 2 = 9, utilizing a easy subtraction.
Nevertheless, the psychological representations of those issues are very totally different, and the researchers needed to find out whether or not the kind of representations may predict the calculation technique, in 1 or 3 steps, of those that clear up them.
“Our speculation was that cardinal issues – such because the one involving marbles – would encourage cardinal drawings, i.e. diagrams with equivalent particular person components, akin to crosses or circles, or with overlaps of components in units or subsets.
Equally, we assumed that ordinal issues – such because the one mentioning journey occasions – would result in ordinal representations, i.e. diagrams with axes, graduations or intervals – and that these ordinal drawings would replicate individuals’ representations and point out that they’d be extra profitable in figuring out the one-step answer technique,’’ explains Hippolyte Gros, former post-doctoral fellow at UNIGE’s College of Psychology and Instructional Sciences, affiliate professor at CYU, and first creator of the examine.
Figuring out psychological representations by way of drawings
These hypotheses had been validated by analyzing the drawings of 52 adults and 59 youngsters.
‘‘We’ve proven that, no matter their expertise – for the reason that identical outcomes had been obtained in each youngsters and adults – the usage of methods by the individuals depends upon their illustration of the issue, and that that is influenced by the non-mathematical info contained in the issue assertion, as revealed by their drawings,’’ says Emmanuel Sander, full professor on the UNIGE’s College of Psychology and Instructional Sciences.
‘‘Our examine additionally reveals that, even after years of expertise in fixing addition and subtraction, the distinction between cardinal and ordinal issues stays very marked. The vast majority of individuals had been solely in a position to clear up issues of the second kind in a single step’’.
Bettering mathematical studying by way of drawing evaluation
The workforce additionally famous that drawings exhibiting ordinal representations had been extra steadily related to a one-step answer, even when the issue was cardinal. In different phrases, drawing with a scale or an axis is linked to the selection of the quickest calculation.
“From a pedagogical standpoint, this implies that the presence of particular options in a pupil’s drawing could or could not point out that his or her illustration of the issue is essentially the most environment friendly one for assembly the directions – on this case, fixing with the fewest calculations doable,” observes Jean-Pierre Thibaut, full professor on the uB Laboratory for Analysis on Studying and Improvement.
‘‘Thus, in relation to subtracting particular person components, a illustration through an axis – moderately than through subsets – is more practical to find the quickest methodology. Evaluation of scholars’ drawings in arithmetic can due to this fact allow focused intervention to assist them translate issues into extra optimum representations.
“A method of doing that is to work on the graphical illustration of statements at school, to assist college students perceive essentially the most direct methods,’’ concludes Hippolyte Gros.
About this math, artwork, and problem-solving analysis information
Writer: Antoine Guenot
Supply: College of Geneva
Contact: Antoine Guenot – College of Geneva
Picture: The picture is credited to Hippolyte Gros
Authentic Analysis: Closed entry.
“Uncovering the interaction between drawings, psychological representations, and arithmetic problem-solving methods in youngsters and adults” by Hippolyte Gros et al. Reminiscence and Cognition
Summary
Uncovering the interaction between drawings, psychological representations, and arithmetic problem-solving methods in youngsters and adults
There may be an ongoing debate within the scientific group concerning the character and position of the psychological representations concerned in fixing arithmetic phrase issues.
On this examine, we took a better take a look at the interaction between psychological representations, drawing manufacturing, and technique alternative. We used dual-strategy isomorphic phrase issues sharing the identical mathematical construction, however differing within the entities they talked about of their downside assertion.
As a result of non-mathematical information connected to those entities, some issues had been believed to result in a selected (cardinal) encoding suitable with one fixing technique, whereas different issues had been thought to foster a unique (ordinal) encoding suitable with the opposite fixing technique.
We requested 59 youngsters and 52 adults to resolve 12 of these arithmetic phrase issues and to make a diagram of every downside. We hypothesized that the diagrams of each teams would show prototypical options indicating both a cardinal illustration or an ordinal illustration, relying on the entities talked about in the issue assertion.
Joint evaluation of the drawing job and the problem-solving job confirmed that the cardinal and ordinal options of the diagrams are linked with the hypothesized semantic properties of the issues and, crucially, with the selection of 1 fixing technique over one other.
We confirmed that no matter their expertise, individuals’ technique use depends upon their downside illustration, which is influenced by the non-mathematical info in the issue assertion, as revealed of their diagrams. We talk about the relevance of drawing duties for investigating psychological representations and fostering mathematical improvement at school.
[ad_2]